dbt Incremental Models: Efficient Transformations
In modern data warehouses, transforming billions of rows daily becomes expensive and time-consuming when using traditional full-refresh approaches. dbt incremental models solve this challenge by processing only new or changed records, dramatically reducing compute costs and transformation times. 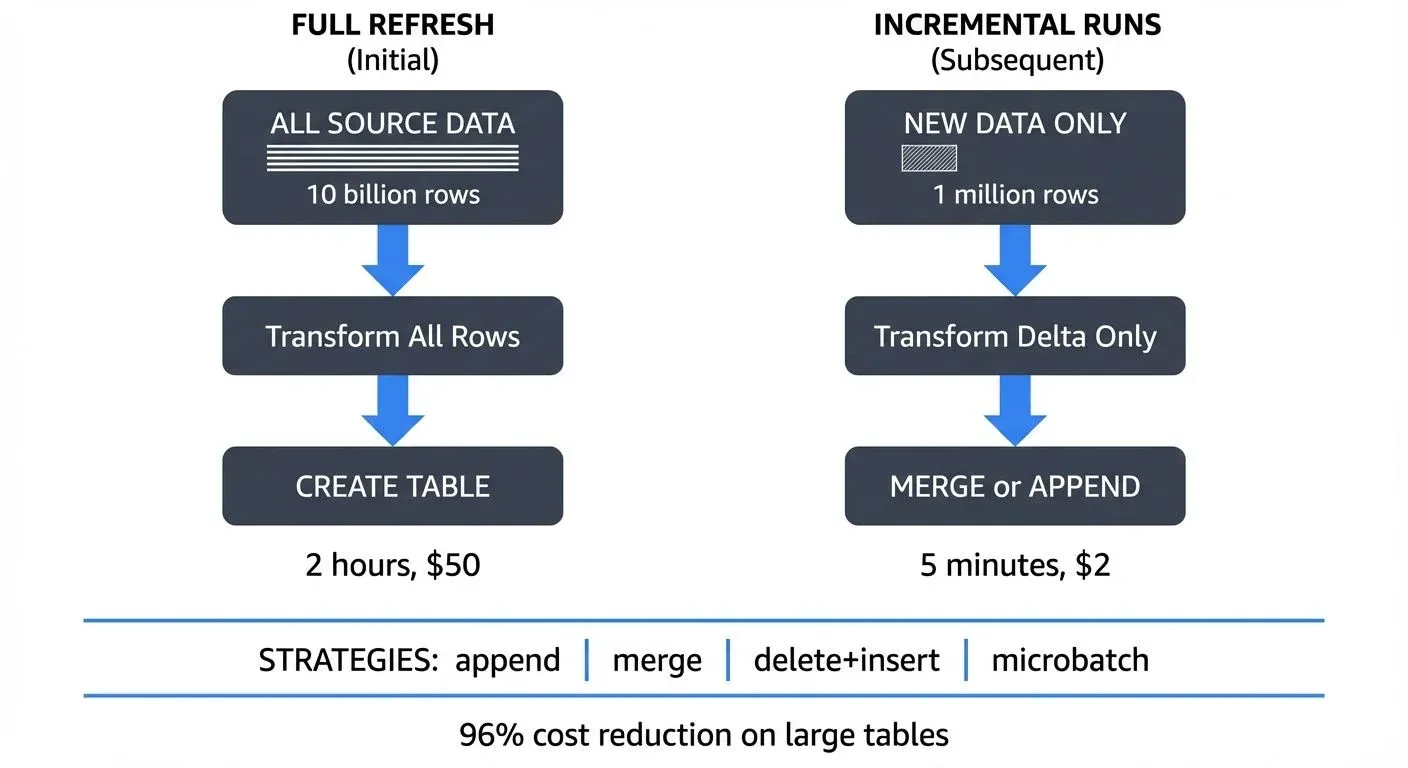
Understanding Incremental Models
Incremental models operate on a simple but powerful principle: instead of rebuilding entire tables from scratch, they identify and process only the delta, the new or modified records since the last run. This approach transforms what might be hour-long jobs into minute-long operations.
Consider a typical scenario: you have an events table with billions of historical records. A full refresh would reprocess every single event, even though only today's data has changed. An incremental model processes just today's events, appending or merging them into the existing table.
Basic Incremental Configuration
Let's start with a fundamental incremental model:
{{
config(
materialized='incremental',
unique_key='event_id'
)
}}
SELECT
event_id,
user_id,
event_type,
event_timestamp,
properties
FROM {{ source('raw', 'events') }}
{% IF is_incremental() %}
WHERE event_timestamp > (SELECT MAX(event_timestamp) FROM {{ this }})
{% endif %}This example uses dbt's Jinja templating syntax (the double curly braces {{ }}), which allows dynamic SQL generation. The is_incremental() macro is crucial, it returns false on the first run, building the full table. On subsequent runs, it returns true, triggering the filter that selects only new records. The {{ this }} reference is a special variable pointing to the current model's table in your data warehouse.
Merge Strategies Explained
dbt supports multiple strategies for handling incremental updates, each suited to different use cases.
Append Strategy
The simplest approach, new rows are added without checking for duplicates:
{{
config(
materialized='incremental',
incremental_strategy='append'
)
}}
SELECT
event_id,
occurred_at,
event_data
FROM {{ source('kafka', 'raw_events') }}
{% IF is_incremental() %}
WHERE occurred_at > (SELECT MAX(occurred_at) FROM {{ this }})
{% endif %}When to use append: Choose this strategy for truly immutable event streams where:
- Each record represents a point-in-time event that never changes (clicks, page views, transactions)
- Duplicates are impossible by design, or deduplication happens in an earlier pipeline stage
- You need maximum write performance since no uniqueness checks occur
Merge Strategy
The merge strategy (default for Snowflake, BigQuery, Databricks) uses unique_key to update existing records and insert new ones:
{{
config(
materialized='incremental',
unique_key='user_id',
incremental_strategy='merge'
)
}}
SELECT
user_id,
email,
last_login_at,
total_purchases,
updated_at
FROM {{ source('app_db', 'users') }}
{% IF is_incremental() %}
WHERE updated_at > (SELECT MAX(updated_at) FROM {{ this }})
{% endif %}This executes as a MERGE statement (or equivalent), perfect for slowly changing dimensions where records update over time.
When to use merge: Choose this strategy when:
- Records can be updated after initial creation (user profiles, order statuses, product catalogs)
- You need to maintain the latest version of each record
- Your data warehouse supports efficient merge operations (most modern warehouses do)
Delete+Insert Strategy
For data warehouses lacking efficient merge operations (like Redshift), delete+insert removes matching records before inserting new ones:
{{
config(
materialized='incremental',
unique_key='order_id',
incremental_strategy='delete+insert'
)
}}
SELECT
order_id,
customer_id,
order_status,
order_total,
updated_at
FROM {{ source('postgres', 'orders') }}
{% IF is_incremental() %}
WHERE updated_at >= CURRENT_DATE - interval '7 days'
{% endif %}This strategy processes batches (like the last 7 days) and completely refreshes those records, handling late-arriving updates effectively.
When to use delete+insert: Choose this strategy when:
- Your warehouse lacks efficient merge operations (older Redshift clusters)
- You need to handle late-arriving data within a specific window
- You want transactional consistency within each batch
Microbatch Strategy (2025 Best Practice)
For time-series data, dbt 1.6+ introduced the microbatch strategy, which has become the standard approach for incremental processing in 2025:
{{
config(
materialized='incremental',
incremental_strategy='microbatch',
unique_key='event_id',
event_time='event_timestamp',
batch_size='hour'
)
}}
SELECT
event_id,
user_id,
event_type,
event_timestamp,
session_data
FROM {{ source('raw', 'events') }}Microbatch automatically divides your data into time-based batches and processes them independently. This provides:
- Automatic backfill orchestration: dbt handles missing time periods intelligently
- Parallel processing: Multiple batches can run simultaneously
- Idempotent reruns: Each batch produces identical results regardless of execution timing
- Built-in late data handling: Overlapping windows catch late arrivals without custom logic
When to use microbatch: This is the recommended approach for any time-series data with consistent timestamps, logs, events, IoT sensor data, or streaming analytics.
Streaming Integration with Kafka
Modern analytics pipelines increasingly integrate streaming data. When connecting dbt to Kafka topics, incremental models become essential for managing continuous data flows.
Conduktor provides enterprise-grade Kafka management, allowing you to monitor, transform, and route streaming data with features like schema registry integration, data quality rules, and real-time governance. Learn more about managing Kafka topics and Kafka Connect for streaming-to-warehouse pipelines. When paired with dbt incremental models, you can efficiently transform streaming data into analytics-ready tables:
{{
config(
materialized='incremental',
unique_key=['event_id', 'partition'],
incremental_strategy='append',
on_schema_change='sync_all_columns'
)
}}
WITH kafka_stream AS (
SELECT
value:event_id::varchar AS event_id, -- :: is Snowflake's cast operator
value:user_id::varchar AS user_id,
value:action::varchar AS action,
to_timestamp(value:TIMESTAMP::bigint) AS event_timestamp,
_partition AS PARTITION, -- Kafka metadata columns from connector
_offset AS kafka_offset
FROM {{ source('kafka_connector', 'user_activity_topic') }}
{% IF is_incremental() %}
WHERE _offset > (SELECT MAX(kafka_offset) FROM {{ this }})
{% endif %}
)
SELECT
event_id,
user_id,
action,
event_timestamp,
PARTITION,
kafka_offset,
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() AS processed_at
FROM kafka_streamKey concepts explained:
- Kafka offsets: Sequential IDs for each message in a partition. Using offsets as your incremental filter guarantees exactly-once processing, each message is processed exactly one time, preventing duplicates or missing data.
- Schema evolution handling: The
on_schema_change='sync_all_columns'option automatically adds new columns when your Kafka topic schema changes, preventing pipeline failures. - Metadata columns: Most Kafka connectors (like Snowflake's Kafka connector) expose
_partitionand_offsetas columns, enabling offset-based incremental processing.
For production Kafka integration, use Conduktor's schema registry to manage Avro/Protobuf schemas and enforce data contracts across your streaming pipeline.
Performance Optimization Patterns
Partitioned Tables
Combine incremental models with table partitioning for maximum efficiency. This BigQuery example shows the configuration syntax:
{{
config(
materialized='incremental',
unique_key='transaction_id',
partition_by={
"field": "transaction_date",
"data_type": "DATE",
"granularity": "DAY"
}
)
}}This limits scans to relevant partitions, dramatically reducing query costs. For example, querying last week's transactions scans only 7 partitions instead of the entire table, a typical cost reduction of 90%+ for large historical tables.
Other warehouse syntax:
- Snowflake: Use
cluster_by=['date_column']for automatic clustering - Databricks: Specify partitioning in table properties:
partition_cols=['date']
Clustered Keys
Add clustering for frequently filtered columns:
{{
config(
materialized='incremental',
unique_key='session_id',
cluster_by=['user_id', 'session_start']
)
}}Lookback Windows
For late-arriving data, implement lookback windows:
{% IF is_incremental() %}
WHERE event_date >= (SELECT MAX(event_date) - interval '3 days' FROM {{ this }})
{% endif %}This reprocesses the last 3 days, catching late arrivals while avoiding full refreshes. Late data arrives due to:
- Clock skew: Different systems having slightly different time clocks
- Network delays: Temporary connectivity issues causing message delays
- Data pipeline latency: Upstream processing taking longer than expected
Incremental Predicates (dbt 1.7+)
For more efficient filtering, especially with partitioned tables, use incremental predicates to push filters down to the source query:
{{
config(
materialized='incremental',
unique_key='order_id',
incremental_predicates=[
"date_partition >= dateadd(DAY, -3, CURRENT_DATE)"
]
)
}}
SELECT * FROM {{ ref('staging_orders') }}
{% IF is_incremental() %}
WHERE updated_at > (SELECT MAX(updated_at) FROM {{ this }})
{% endif %}The incremental_predicates filter applies to both the source data and the existing table during merge operations, reducing the amount of data scanned.
Testing and Monitoring
Always implement tests for incremental models:
models:
- name: incremental_events
tests:
- dbt_utils.recency:
datepart: hour
field: event_timestamp
interval: 2
columns:
- name: event_id
tests:
- unique
- not_null2025 Monitoring Options:
- dbt Cloud: Built-in observability with model timing, row counts, and test results
- Elementary Data: Open-source data observability that monitors anomalies, schema changes, and data quality issues directly in your warehouse
- dbt Mesh: For large organizations, implement cross-project dependencies and centralized monitoring across multiple dbt projects
- Custom macros: Log metrics (row counts, runtime, error rates) to dedicated monitoring tables for trend analysis
Real-world example: A properly configured incremental model on a 5 billion row events table reduces processing from 2 hours (full refresh, $50 in compute) to 5 minutes (incremental, $2 in compute), a 96% cost reduction.
When NOT to Use Incremental Models
While incremental models offer significant benefits, they're not always the right choice:
- Small tables (< 1 million rows): Full refresh is simpler and fast enough
- Frequently changing dimensions: If >50% of rows update each run, full refresh may be faster
- Complex business logic: When your transformation logic itself changes frequently, full refreshes ensure consistency
- Initial development: Start with full refresh (
materialized='table'), then optimize to incremental once logic stabilizes
Consider dbt snapshots (Type 2 Slowly Changing Dimensions) instead of incremental models when you need to track the full history of how records change over time, not just the current state.
Common Pitfalls and Troubleshooting
- Forgetting the initial load: Always test your model with a full refresh (
dbt run --full-refresh) to ensure it works without the incremental filter. - Ignoring idempotency: Incremental models should produce identical results whether run once or multiple times, critical for backfills and reruns. Test this by running your model twice and comparing results.
- Over-relying on timestamps: Late-arriving data can cause missed records. Solutions:
- Use sequence numbers or Kafka offsets instead of timestamps when available
- Implement lookback windows to reprocess recent data
- Use the microbatch strategy which handles this automatically
- Common error: "Compilation Error in model": Usually indicates syntax errors in Jinja logic. Check that all
{% if %}blocks have matching{% endif %}tags. - Duplicate records despite unique_key: Verify your unique_key is truly unique with a test. Composite keys require list syntax:
unique_key=['col1', 'col2'].
Conclusion
Incremental models represent a fundamental shift from batch-oriented to continuous transformation patterns. By processing only what's changed, they enable real-time analytics at scale while controlling costs. Whether you're integrating Kafka streams with Conduktor or transforming traditional database changes, mastering incremental strategies is essential for modern analytics engineering.
Quick decision guide:
- Immutable events → Use
microbatch(2025 best practice) orappend - Updating dimensions → Use
merge - Late-arriving data in batches → Use
delete+insert - Real-time streams → Use
appendwith Kafka offsets
Start with simple strategies for immutable events, graduate to merge strategies for changing dimensions, and leverage streaming offsets for real-time pipelines. With proper testing, monitoring via Elementary Data or dbt Cloud, and the right incremental strategy, you can achieve 90%+ cost reductions while maintaining data freshness.
Related Concepts
- dbt Tests and Data Quality Checks - Validating incremental models to ensure data quality
- Streaming ETL vs Traditional ETL - How incremental models bridge batch and streaming paradigms
- Data Contracts for Reliable Pipelines - Defining expectations for incremental model inputs
Sources and References
- dbt Documentation: Incremental Models
- dbt Microbatch Strategy Guide
- dbt Best Practices: Incremental Model Strategies
- Apache Kafka Consumer Offsets Documentation
- Conduktor Platform: Kafka Management and Governance
- Elementary Data: Open-Source Data Observability
- Snowflake MERGE Statement Guide
- dbt Snapshots Documentation
Written by Stéphane Derosiaux · Last updated March 9, 2026