GDPR Compliance for Data Teams: Navigating Privacy in Modern Data Architectures
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has fundamentally transformed how organizations handle personal data. For data teams working with modern streaming architectures and distributed systems, compliance presents unique technical challenges that go beyond traditional database management.
- Who Does GDPR Apply To? GDPR applies to any organization that processes personal data of EU residents, regardless of where the organization is located. This includes both "data controllers" (who determine purposes and means of processing) and "data processors" (who process data on behalf of controllers).
- What Are the Penalties for Non-Compliance? GDPR violations can result in fines of up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher. Beyond financial penalties, non-compliance can lead to reputational damage, loss of customer trust, and operational disruptions. As of 2025, enforcement has intensified, with regulators actively monitoring AI/ML data usage.
This article explores practical strategies and technical implementations for achieving GDPR compliance in data-intensive streaming environments. 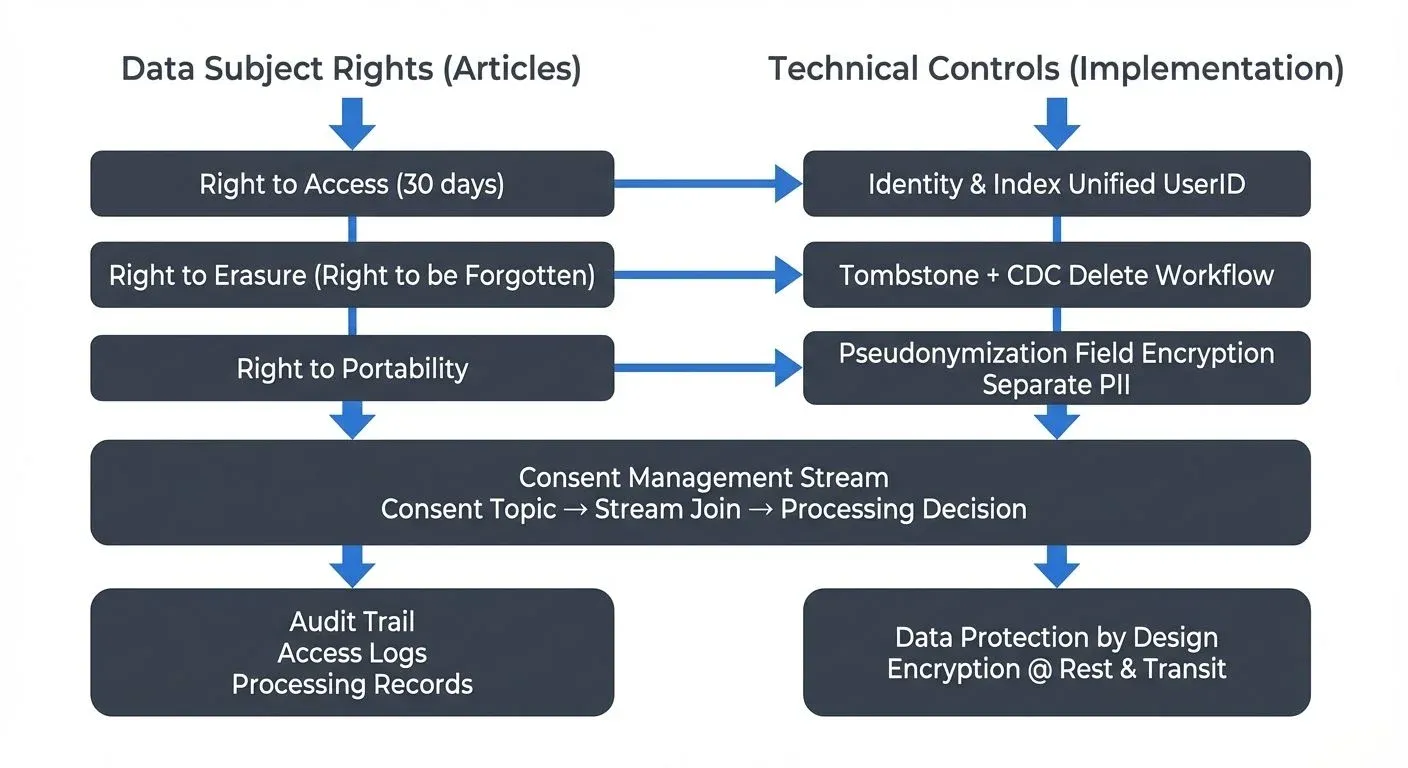
Key GDPR Timelines for Data Teams:
- 30 days: Maximum time to fulfill data subject access requests (DSARs)
- 72 hours: Required notification window for data breaches to supervisory authorities
- 1 month: Default timeframe to respond to data subject requests (erasure, rectification, etc.)
- Without undue delay: Obligation to inform data subjects of breaches when they're at high risk
Understanding GDPR's Core Principles for Data Teams
GDPR establishes seven foundational principles that data teams must embed into their technical architecture: lawfulness, fairness, and transparency; purpose limitation; data minimization; accuracy; storage limitation; integrity and confidentiality; and accountability. These principles translate into specific technical requirements that affect every layer of your data infrastructure.
The principle of data minimization requires teams to collect only what is necessary for specific purposes. In practice, this means implementing schema validation and filtering mechanisms at ingestion points. For streaming platforms like Apache Kafka, this might involve deploying data governance tools that enforce field-level policies before messages reach downstream consumers. For guidance on detecting and handling sensitive data in streams, see PII Detection and Handling in Event Streams and PII Leakage Prevention.
Storage limitation demands that personal data be retained only as long as necessary. Data teams must implement automated retention policies with configurable time-to-live (TTL) settings across all storage layers, from streaming platforms to data warehouses and analytics databases.
Technical Implementation of Data Subject Rights
GDPR grants individuals eight fundamental rights regarding their personal data. For data teams, the most technically challenging are the right to access, right to rectification, right to erasure (the "right to be forgotten"), and right to data portability.
Right to Access and Portability
When a data subject requests access to their personal data, your systems must be capable of identifying and retrieving all records across distributed systems within the GDPR-mandated 30-day window. This requires:
- Unified identity management: Implement a consistent user identifier schema across all systems to enable efficient data retrieval
- Data catalog and lineage tracking: Maintain comprehensive metadata about where personal data resides and how it flows through your pipeline. For detailed coverage of data cataloging, see What is a Data Catalog: Modern Data Discovery
- Export mechanisms: Build automated processes to extract, format, and deliver data in machine-readable formats (typically JSON or CSV)
Right to Erasure: The Streaming Challenge
The right to be forgotten presents particular challenges in streaming architectures where data is immutable by design. Apache Kafka, for instance, uses append-only logs that cannot be modified retroactively without compromising the integrity of the event stream.
Data teams have several architectural options to address this:
Tombstone Records: A tombstone is a special message with a null value that signals a deletion. When published to Kafka topics with a specific key (e.g., user ID), it marks that key's data for removal. Downstream consumers must implement logic to honor these tombstones and filter out deleted records during processing.
Here's a practical implementation for handling the right to erasure in streaming systems:
from kafka import KafkaProducer, KafkaConsumer
import json
from datetime import datetime
class DataDeletionManager:
def __init__(self, bootstrap_servers):
self.producer = KafkaProducer(
bootstrap_servers=bootstrap_servers,
value_serializer=lambda v: json.dumps(v).encode('utf-8') if v else None
)
self.deletion_topic = 'user-deletion-requests'
def process_deletion_request(self, user_id):
"""Process right to erasure request for a user."""
# Step 1: Publish tombstone to user data topics
self.producer.send(
'user-events',
key=user_id.encode('utf-8'),
value=None # Tombstone record
)
# Step 2: Record deletion event for audit trail
deletion_event = {
'user_id': user_id,
'timestamp': datetime.utcnow().isoformat(),
'requested_by': 'data_subject',
'status': 'initiated'
}
self.producer.send(self.deletion_topic, value=deletion_event)
# Step 3: Delete from databases and data warehouses
self._delete_from_databases(user_id)
# Step 4: Remove PII from separate PII store
self._delete_pii_mapping(user_id)
self.producer.flush()
return {'user_id': user_id, 'status': 'deletion_initiated'}
def _delete_from_databases(self, user_id):
"""Delete user data from all databases."""
# Example: PostgreSQL deletion
# NOTE: Use environment variables or secure credential management (e.g., AWS Secrets Manager, HashiCorp Vault)
import psycopg2
import os
conn = psycopg2.connect(
dbname=os.getenv('DB_NAME'),
user=os.getenv('DB_USER'),
password=os.getenv('DB_PASSWORD'),
host=os.getenv('DB_HOST')
)
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute("DELETE FROM user_profiles WHERE user_id = %s", (user_id,))
cursor.execute("DELETE FROM user_events WHERE user_id = %s", (user_id,))
conn.commit()
conn.close()
def _delete_pii_mapping(self, user_id):
"""Remove PII mapping for pseudonymization."""
# Delete from PII vault/store
pass
class TombstoneAwareConsumer:
def __init__(self, bootstrap_servers, topic):
self.consumer = KafkaConsumer(
topic,
bootstrap_servers=bootstrap_servers,
value_deserializer=lambda m: json.loads(m.decode('utf-8')) if m else None
)
self.deleted_users = set()
def process_messages(self):
"""Process messages while respecting tombstones."""
for message in self.consumer:
if message.value is None:
# Tombstone detected - record deleted user
user_id = message.key.decode('utf-8')
self.deleted_users.add(user_id)
print(f"User {user_id} has been deleted - skipping all future events")
else:
# Regular event - check if user is deleted
user_id = message.value.get('user_id')
if user_id not in self.deleted_users:
self._process_event(message.value)
else:
print(f"Skipping event for deleted user {user_id}")
def _process_event(self, event):
"""Process valid event."""
pass
# Usage
deletion_mgr = DataDeletionManager(['localhost:9092'])
deletion_mgr.process_deletion_request('user-123')- Data Pseudonymization: Store personal identifiable information (PII) separately from event data, using tokenized references. When deletion is requested, remove the PII mapping while preserving anonymized event history for analytics.
- Log Compaction with Key-Based Deletion: Configure Kafka topics with log compaction enabled. When a deletion request arrives, publish a tombstone record with the user's identifier as the key, allowing Kafka to eventually remove all records for that key. For detailed coverage of log compaction mechanics, see Kafka Log Compaction Explained.
- Policy Enforcement Layer: Data governance platforms like Conduktor provide capabilities that enable teams to implement deletion policies, data masking, and field-level encryption across Kafka clusters. Conduktor's policy enforcement features can intercept, filter, and transform messages based on compliance rules without requiring changes to producer or consumer applications, making GDPR compliance enforcement more manageable at scale.
Consent Management in Streaming Systems
GDPR requires explicit, informed consent before processing personal data for specific purposes. Data teams must implement consent as a first-class attribute in their data models.
In streaming architectures, consent should be treated as event data itself. When a user grants or revokes consent, publish a consent event to a dedicated topic. Downstream processors can then join stream data with the latest consent state to determine whether processing is lawful.
Consider this approach:
- Consent Events Topic: Maintain a compacted topic containing the latest consent preferences for each user
- Stream Enrichment: Join data streams with consent state before processing
- Conditional Processing: Implement stream processors that route data based on consent status, processing consented data normally while quarantining or dropping non-consented data
Here's a practical example of consent event publishing and validation:
from kafka import KafkaProducer
import json
from datetime import datetime
class ConsentManager:
def __init__(self, bootstrap_servers):
self.producer = KafkaProducer(
bootstrap_servers=bootstrap_servers,
value_serializer=lambda v: json.dumps(v).encode('utf-8')
)
self.consent_topic = 'user-consent-events'
def record_consent(self, user_id, purposes, granted=True):
"""Record user consent for specific data processing purposes."""
consent_event = {
'user_id': user_id,
'timestamp': datetime.utcnow().isoformat(),
'purposes': purposes, # e.g., [_7_, _8_]
'granted': granted,
'consent_version': '1.0'
}
# Use user_id as key for log compaction
self.producer.send(
self.consent_topic,
key=user_id.encode('utf-8'),
value=consent_event
)
self.producer.flush()
def revoke_consent(self, user_id, purposes):
"""Revoke user consent for specific purposes."""
self.record_consent(user_id, purposes, granted=False)
# Usage
consent_mgr = ConsentManager(['localhost:9092'])
consent_mgr.record_consent('user-123', ['marketing', 'analytics'], granted=True)Stream processors can then validate consent before processing personal data:
from kafka import KafkaConsumer
import json
class ConsentAwareProcessor:
def __init__(self, bootstrap_servers):
# Consumer for consent state (compacted topic)
self.consent_consumer = KafkaConsumer(
'user-consent-events',
bootstrap_servers=bootstrap_servers,
value_deserializer=lambda m: json.loads(m.decode('utf-8')),
auto_offset_reset='earliest'
)
# Build consent state cache
self.consent_cache = {}
self._load_consent_state()
def _load_consent_state(self):
"""Load latest consent state for all users."""
for message in self.consent_consumer:
user_id = message.key.decode('utf-8')
consent_data = message.value
self.consent_cache[user_id] = consent_data
def can_process(self, user_id, purpose):
"""Check if we have consent to process data for given purpose."""
consent = self.consent_cache.get(user_id)
if not consent:
return False
return consent.get('granted', False) and purpose in consent.get('purposes', [])
def process_event(self, event):
"""Process event only if consent is granted."""
user_id = event.get('user_id')
if self.can_process(user_id, 'analytics'):
# Process the event
return self._perform_analysis(event)
else:
# Drop or quarantine the event
return NoneData Protection by Design and Default
Article 25 of GDPR requires "data protection by design and default," meaning privacy considerations must be integrated into systems from the earliest development stages.
For data teams, this translates into:
- Encryption at Rest and in Transit: All personal data must be encrypted using industry-standard algorithms (AES-256 for storage, TLS 1.3 for transmission)
- Field-Level Encryption: Encrypt specific PII fields while leaving non-sensitive data plaintext for analytics. This enables you to maintain data utility while protecting privacy.
- Key Management: Enterprise GDPR compliance requires robust key management using services like AWS Key Management Service (KMS), Azure Key Vault, Google Cloud KMS, or HashiCorp Vault. These services provide key rotation, access auditing, and centralized control essential for regulatory compliance. Never hardcode encryption keys in application code.
Here's an implementation example for field-level encryption in streaming data:
from cryptography.fernet import Fernet
from kafka import KafkaProducer, KafkaConsumer
import json
import base64
class FieldEncryptor:
def __init__(self, encryption_key=None):
"""Initialize with encryption key or generate new one."""
if encryption_key:
self.key = encryption_key
else:
self.key = Fernet.generate_key()
self.cipher = Fernet(self.key)
def encrypt_fields(self, data, sensitive_fields):
"""Encrypt specified fields in the data dictionary."""
encrypted_data = data.copy()
for field in sensitive_fields:
if field in encrypted_data:
# Encrypt the field value
plaintext = str(encrypted_data[field]).encode('utf-8')
encrypted_value = self.cipher.encrypt(plaintext)
encrypted_data[field] = base64.b64encode(encrypted_value).decode('utf-8')
# Mark field as encrypted for downstream processing
encrypted_data[f'{field}_encrypted'] = True
return encrypted_data
def decrypt_fields(self, data, sensitive_fields):
"""Decrypt specified fields in the data dictionary."""
decrypted_data = data.copy()
for field in sensitive_fields:
if field in decrypted_data and decrypted_data.get(f'{field}_encrypted'):
# Decrypt the field value
encrypted_value = base64.b64decode(decrypted_data[field])
plaintext = self.cipher.decrypt(encrypted_value)
decrypted_data[field] = plaintext.decode('utf-8')
del decrypted_data[f'{field}_encrypted']
return decrypted_data
# Usage in Kafka producer
encryptor = FieldEncryptor()
producer = KafkaProducer(
bootstrap_servers=['localhost:9092'],
value_serializer=lambda v: json.dumps(v).encode('utf-8')
)
# User event with PII
user_event = {
'user_id': 'user-123',
'email': 'user@example.com',
'name': 'John Doe',
'activity': 'page_view',
'timestamp': datetime.utcnow().isoformat() + 'Z'
}
# Encrypt sensitive fields before publishing
sensitive_fields = ['email', 'name']
encrypted_event = encryptor.encrypt_fields(user_event, sensitive_fields)
producer.send('user-events', value=encrypted_event)- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Implement granular permissions that restrict access to personal data based on job function and necessity. Modern data governance platforms provide fine-grained access controls at the topic, consumer group, and even field level. For comprehensive guidance on implementing access controls in Kafka, see Kafka ACLs and Authorization Patterns and Kafka Authentication: SASL, SSL, OAuth.
- Data Masking and Redaction: Automatically mask or redact sensitive fields when data moves to non-production environments or when accessed by roles without appropriate clearance.
Audit Trails and Accountability
GDPR's accountability principle requires organizations to demonstrate compliance through comprehensive documentation. Data teams must implement:
- Access Logging: Record every access to personal data, including who accessed it, when, what data was accessed, and for what purpose. For implementation patterns, see Streaming Audit Logs
- Processing Records: Maintain detailed records of all data processing activities, including data sources, purposes, categories of recipients, and retention periods
- Schema Evolution Tracking: Document all changes to data structures that contain personal data, ensuring you can trace how data models evolved over time
- Automated Compliance Reports: Build dashboards and reporting mechanisms that provide real-time visibility into compliance posture, including retention policy adherence, consent rates, and data subject request fulfillment metrics
2025 GDPR Enforcement: AI/ML and Automation
As of 2025, GDPR enforcement has evolved to address modern data processing challenges, particularly around artificial intelligence and machine learning systems.
AI/ML Data Processing Requirements
When training machine learning models on personal data, GDPR requires:
- Explicit Consent for AI Training: Data subjects must explicitly consent to their data being used for AI/ML model training, separate from other processing purposes
- Model Explainability: Organizations must be able to explain automated decision-making processes to data subjects (Article 22 - Right to Explanation)
- Training Data Lineage: Maintain comprehensive records of which personal data was used to train which models and when
- Model Retraining After Deletion: When users exercise the right to be forgotten, organizations may need to retrain models that were trained on their data
Here's a practical approach to tracking consent for AI/ML processing:
class MLConsentManager:
def __init__(self, bootstrap_servers):
self.producer = KafkaProducer(
bootstrap_servers=bootstrap_servers,
value_serializer=lambda v: json.dumps(v).encode('utf-8')
)
self.ml_consent_topic = 'ml-training-consent'
def record_ml_consent(self, user_id, model_purpose, granted=True):
"""Record consent specifically for ML model training."""
consent_event = {
'user_id': user_id,
'timestamp': datetime.utcnow().isoformat(),
'model_purpose': model_purpose, # e.g., _7_, _8_
'granted': granted,
'consent_version': '2.0',
'ai_training': True # Flag for AI/ML specific consent
}
self.producer.send(
self.ml_consent_topic,
key=user_id.encode('utf-8'),
value=consent_event
)
self.producer.flush()
def log_training_data_usage(self, model_id, user_ids):
"""Track which user data was used to train which models."""
training_event = {
'model_id': model_id,
'timestamp': datetime.utcnow().isoformat(),
'user_count': len(user_ids),
'user_ids': user_ids[:100], # Sample for audit purposes
'event_type': 'model_training'
}
self.producer.send('ml-audit-trail', value=training_event)
self.producer.flush()Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) Automation
The 30-day window for fulfilling data subject access requests (DSARs) has driven automation requirements in 2025:
- Automated Data Discovery: Tools that automatically scan data stores to locate personal data across distributed systems
- Self-Service DSAR Portals: User-facing interfaces where data subjects can submit requests and track progress
- Orchestrated Deletion Workflows: Automated workflows that ensure deletion propagates across all systems (streaming platforms, databases, backups, and ML models)
- Compliance Monitoring: Real-time dashboards tracking DSAR fulfillment rates and identifying bottlenecks
Modern data governance platforms like Conduktor now include DSAR automation features that integrate with streaming platforms to streamline the request fulfillment process.
Building a Compliant Streaming Architecture
Modern data teams working with streaming platforms must architect for compliance from the ground up. A compliant streaming architecture typically includes:
- Ingestion Layer: Data validation, schema enforcement, and initial consent verification
- Governance Layer: Policy enforcement, data classification, and transformation rules
- Processing Layer: Stream processors that honor consent, implement retention policies, and respect data subject rights
- Storage Layer: Encrypted, access-controlled data stores with automated retention and deletion
- Audit Layer: Comprehensive logging and monitoring of all data access and processing activities
Conclusion
GDPR compliance for data teams is not merely a legal checkbox, it's an opportunity to build more robust, trustworthy, and well-architected data systems. By treating privacy as a core architectural requirement rather than an afterthought, data teams can create streaming platforms that respect user rights while delivering business value.
The technical challenges are significant, particularly around implementing the right to erasure in immutable event streams and managing consent across distributed systems. However, with careful architectural planning, appropriate tooling for governance enforcement, and a commitment to privacy by design, data teams can build systems that are both GDPR-compliant and technically excellent.
As data regulations continue to evolve globally, the investments you make in privacy-centric architecture today will position your organization for success in an increasingly regulated future.
Related Concepts
- PII Detection and Handling in Event Streams - Automated detection and protection of personal data in streaming systems to support GDPR compliance.
- Data Masking and Anonymization for Streaming - Pseudonymization and anonymization techniques required for GDPR Article 32 compliance.
- Audit Logging for Streaming Platforms - Comprehensive audit trails for demonstrating GDPR accountability and tracking data subject requests.
Sources and References
- European Union GDPR Official Text - EUR-Lex - General Data Protection Regulation - The official legal text of the GDPR, providing authoritative guidance on all articles and requirements.
- Information Commissioner's Office (ICO) - Guide to GDPR - ICO GDPR Guide - Comprehensive guidance from the UK's data protection authority on implementing GDPR requirements.
- Apache Kafka Documentation - Security and GDPR - Kafka Security Documentation - Technical documentation on implementing security, encryption, and compliance features in Apache Kafka.
- NIST Special Publication 800-53 - Security and Privacy Controls - US government framework for information security controls applicable to GDPR compliance.
- European Data Protection Board - Guidelines on Data Protection by Design and by Default - EDPB Guidelines - Official guidance on implementing Article 25 requirements for data protection by design.
Written by Stéphane Derosiaux · Last updated March 4, 2026